What are Shear and Bending Moment Diagrams?
Determining the shear and bending moment diagram is a crucial skill that every engineer should master. Without understanding the concept and depth of the shear force and bending moment diagram, you can not complete a design for a building or infrastructure. These diagrams determine the underlying state of stress in the structure. Every engineer needs to understand this because they will always be tested on their concepts of these diagrams. We will give you all the details about shear and bending moment diagrams and their purpose in the following article.
Before getting into the shear and bending moment diagram we need to understand the meaning of shear force and bending moment.
Shear Force
A force acting in a direction parallel to a surface or a planer cross-section of an object or a body is termed a shear force. Shear force is caused by the shearing load acting on the body. There are many examples to explain what a shear force is:
- Force is exerted on the side walls of a building due to the wind.
- The frictional force between the two bodies that are placed on top of each other is also a shear force.
- Transverse force on a beam is also shear force.
Bending moment
It is a rotational force that is generated when a force is exerted perpendicularly to a point at a given distance away from that point. It is calculated as the perpendicular force multiplied by the distance from the point. In simple words, a bending moment is a bend that results in a beam due to a moment.
When you are calculating bending moments, remember these two things:
- The standard units are Nm
- Clockwise bending is taken as negative.
Shear force and bending moment diagrams
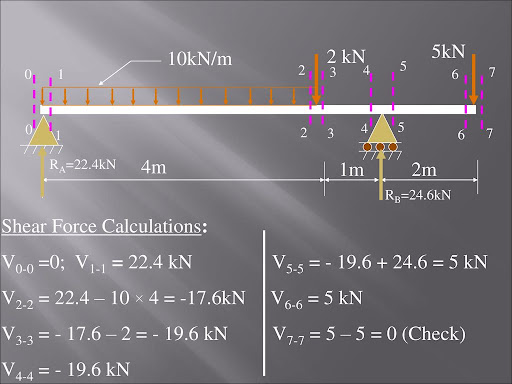
A shear force diagram is a graphical representation of the variation of shear forces along the length of a beam or beam’s longitudinal direction. With the help of a shear force diagram, we can find the value of a shear force at different points of an object. A very important point to note is that a Shear force is equal to the rate of change of bending moment along the section. So, it is clear that shear force will always be one degree lower than the bending moment. For example, when the bending moment is linear, the Shear force will be constant.
A bending moment diagram is a graphical representation of the variations of the bending moment along the beam. The bending moment is nothing but the extent to which a beam is bent when a force is acting on it perpendicularly. So, the bending moment diagram represents all the points of the bending moment on a graph.
Relationship between Shear force and Bending Moment
Both the shear force and bending moment are induced by the effect of the loading over the beams. The variation of shear forces affects the bending moment at a particular section. Therefore, it is clear that a valid relationship must exist between shear force and bending moment.
The mathematical expression of the relationship between shear force and bending moment is expressed as V= dM/dX.
So, the variation of the shear force along the beams is the rate of change of bending moment along the beam.
Purpose of a shear force and bending moment diagram
- The shear force and bending moment diagram can be used to analyze the beam.
- The shear force diagram determines the amount of shear force resisted by the beam section at every point of the beam along its length.
- The bending moment diagram determines the bending moment resisted by the beam section at every point of the beam along its length.
- Shear and bending moment diagrams act as analytical tools. They are used along with the structural analysis to help perform structural design by determining the value of shear force and bending moment at every given point of an element.
- The type, and size of the member of a given material can be easily determined by these diagrams.
- Finally, the shear and moment diagrams can be used to determine the deflection using either the moment area method or the conjugate beam method.